Efforts to improve quality
Policy/view
Establishing a quality management system (hereinafter referred to as "QMS") that conforms to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) based on the total quality management (hereinafter referred to as "TQM") introduced in 1983, our company is making efforts to maintain and improve the manufacturing system. We promote the foundation principle of "gaining a client's confidence by doing a good job" in the fundamental principles of our quality policy. Regarding all stakeholders, such as not only ordering parties but also end users of buildings and residents of local communities, as clients (customers), we are aiming to realize "customer satisfaction" in each position. We established and have been operating the "quality and environmental rules" integrated with the environmental management system (hereinafter referred to as "EMS") since FY 2017.
Management
Our company’s quality management is operated with the Civil Engineering Division manager and the Building Division manager at the top and with the Civil Engineering Department manager and Building Department manager appointed as the operation managers. Also, in the "quality and environmental rules" mentioned above, we provide ten steps of Q0 quality planning - Q2 and 3 design - Q5 contract - Q7 construction - Q10 quality evaluation in a “quality assurance system chart” and hold a review board and a review meeting of DR0-DR6 at each step, and are making efforts to improve failure prevention and customer satisfaction.
We also provide, standardize, and revise, as required, civil engineering technology expertise collections in civil engineering construction and MAEDA standards and MAEDA rules in building work. In addition, we are working on safety management and construction management using information and communications technology (ICT) and building information modeling (BIM), which is a three-dimensional building model. Specifically, we are making efforts to improve the efficiency of various construction-related checks by TPMm (construction management system) and to provide quality buildings by a reliable checking system. For BIM, we prevent the occurrence of a failure by using BIM, in which each related company is involved, and are working on productivity improvement. For the BIM at the construction stage, we are promoting education to disseminate the efforts internally so that they are performed in each field office. Additionally, the BIM/ICT lecture "Use of ICT technologies on building sites" has been established as a WEB lecture for construction employees.
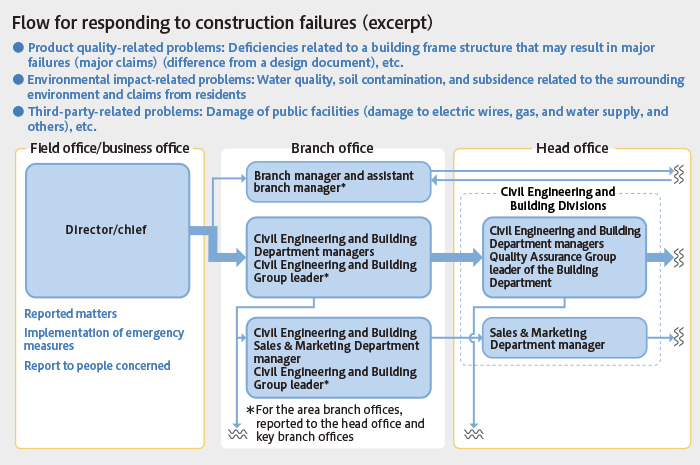
For failures (such as quality, environment , and safety) related to construction, since subsequent actions significantly affect risk, in 2008 our company established the "flow for responding to construction failure," which specifies the response to serious failures, in the following figure. For failures related to construction, information is reported by each field office through the "failure, correction, and preventive action database (DB)." The Civil Engineering Department and the Building Department are examining and considering the content as required, and are conducting horizontal development of the results as measures to prevent a recurrence.
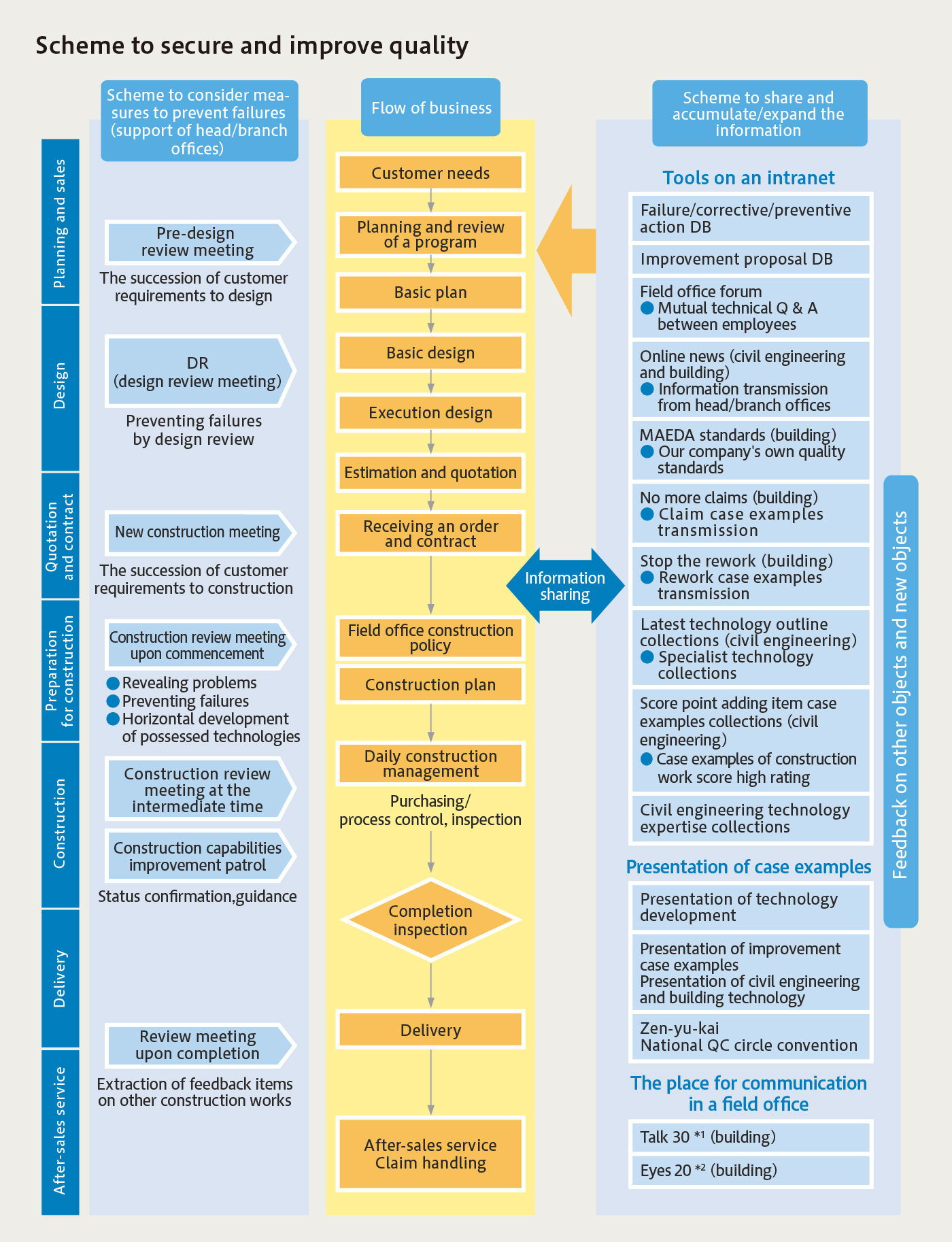
- *1 Talk 30:Meeting at which all on-site employees gather and discuss the problems from failure prevention, construction VE, and improvement activities to on-site problems from different perspectives
- *2 Eyes 20:A place for education that aims at the collective mindset of on-site employees, including cooperative companies, while looking at actual matters on site or for a director, section chiefs, and chiefs to guide junior employees and cooperative suppliers.
Results
Civil Engineering Department
Efforts for quality
Concerning quality, we hold a construction review meeting in accordance with the progress of the construction work, and the head office, branch, and field office are working on quality improvement in an integrated manner. The experienced veteran employees participate in various review meetings etc., the construction management system is reinforced, and a database of quality failure information is created to promote information sharing and prevent accidents.
In FY 2022, review meetings in field offices were held at 98 field offices, 131 times in total.
Conducting training
To realize two strategic pillars, “enhancement of the core business” and “expansion of the business field,” the Civil Engineering Division has been making various efforts to accelerate the human resources development while rotating the cycle of fundamental human resources development.
One of the efforts is the basic rotation of employees in their second to tenth year after joining the company.
Through the rotation, individual employees gain various experiences through works in various types of construction at various regions ordered by various ordering parties, which is the strength of the civil engineering business, thereby promoting personal growth.
Training plans are devised according to personal characteristics and training matched closely to individuals' needs is provided, which is also one of our characteristic efforts.
The human resources development meeting is positioned at the center of these efforts. The human resources development meeting is held twice a year at each branch and department.
At the meeting, a human resources development policy is discussed based on the efforts of young employees (in their second to fifth year after joining the company) in their works, state of their motivation, degree of their growth, etc. A trainer, people concerned at the head/ branch offices, and a human resources development adviser attend the meetings and share the information. Based on the human resources development policy determined in the meeting, the trainer notifies young employees of the specific content of instructions through an “interview for supporting growth.” The head office, branch offices, and field offices are working to develop young employees in an integrated manner through such efforts.
Since the beginning of the current fiscal year, we have been planning the training not only for young employees, but also for employees in responsible positions by utilizing data, knowledge, and expertise about human resources development accumulated over many years to improve their abilities as superiors.
In this way, a culture for developing human resources has been established by operating the cycle of human resources development while stepping up such cycle.
For the education on quality, management system training is conducted in the fourth year, in addition to new employee training, third-year training, fifth-year training, tenth-year training, and middle managers training, all of which are collective education carried out across the company annually.
In addition to the above training mainly with classroom lectures, we have also provided the “field technical training” using our actual construction sites. In FY 2022, under COVID-19, while conducting physical condition checks, antigen tests before and after training, etc., we implemented the training nine times, in which a total of over 110 employees participated.
Furthermore, WEB lectures that every employee can attend at any time as required are open to the public.
In FY2021, we opened our internal YouTube channel, and we are putting our efforts into recurrent education as well.
WEB lectures on civil engineering, consisting of technical lectures (such as those about concrete, soil property, and earth retaining) and environmental lectures, are provided in the form of viewing the lecturer’s lecture videos. In FY 2022, we conducted 72 courses, and they were attended 2,784 times in total. To encourage our employees to take the lectures, we have visualized each employee's progress of taking lectures and also indicated the levels of lectures from beginner to manager class. As a result, the number of times the lectures were viewed was more than doubled compared to that of FY2021. In FY2022, the lectures have been partially opened to our cooperating companies and used as training materials for their employees.
More than 120 uploaded videos are available in the internal YouTube channel. The contents include not only the contents directly connected to works, but also the introduction of operations of each department, etc., which support the career formation of employees.

Building Department
We record the number of complaints after completion for each construction work. The number of complaints we received in FY 2021 was 236. When we receive a complaint, the parties involved in the construction work, and related departments of the head office and the branch offices cooperate to investigate and analyze the details, and seek to prevent its reoccurrence.
Efforts for quality
At the intermediate stage of construction, we hold a construction review meeting at the intermediate time. It is confirmed not only whether matters that were decided at a construction review meeting upon commencement have been implemented, whether matters that were not planned at that time have been planned, etc., but also whether laws and regulations have been observed.
In the building stage, employees who have experienced similar cases at field offices and branch offices and persons in charge from related departments of the head office participate in the construction review meeting upon commencement. At the meeting, tasks, problems, and matters to be studied before proceeding with the construction are extracted mainly from design drawings, and measures to be taken for them are appropriately instructed and guidance is given. In FY 2022, the construction review meetings were extracted and conducted at 32 sites (at one site overseas).
In addition, the head office staff and the SE/technical director of branch offices play a central part in the construction capabilities improvement patrol (quality patrol) to secure structural quality and the quality of finishing and equipment. They were conducted at 75 sites, 101 times in total in FY 2022 (part of the participants attended Teams as a measure against COVID-19 infection).
Also for each field office’s efforts for productivity improvement (new efforts, such as those for techniques, construction methods, shortening of the construction period, and ICT utilization, excluding those for a productivity improvement sheet), which were extracted through the construction capability improvement patrol (quality patrol), we take photographs and drawings back to the head office, and show them on the Archisite (website for architectural employees) as case examples for the horizontal development (case examples of failures and those of environmental efforts are also shown). Furthermore, on October 28, FY2022, we held the ‘FY2022 Building Production Technology Presentation,’ introducing the case examples at construction field offices where the originality and ingenuity were exerted and productivity was improved through “labor saving,” “construction period reduction,” etc. as well as the “new technologies” and “new construction methods” developed by the technical development and efforts on BIM at the head office and branch offices. For the presentation, 6 case examples were selected from the applications from 16 worksites around the country.
This presentation is intended to be utilized in the enhancement of employees which are the human capital, deployment of technologies for labor saving and construction period reduction in construction work, and improvement of employees' technical capabilities and motivation. (See the photos below of the Building Production Technology Presentation.)
Since FY 2019, we have checked, during the field office patrol, for the implementation of sketch communication, extraction of reputation risks at the field office, and measures against the risks.
- -Sketch communication ⇒ Developing the "abilities to think, study, and communicate through sketching." We started this activity to maintain and improve engineering capabilities at each field office. Conventionally, similar activities were conducted. By conducting them consciously, workers can recognize anew what is important and improve their engineering capabilities.
- -Extraction of reputation risks at a field office and measures against the risks ⇒ To raise awareness of reputation risks at each field office, we disseminated the information on the present state of reputation risks and case examples to all workers, made them extract reputation risks specific to the field office, and instructed them to take measures against the risks, at the construction review meetings upon commencement and the construction capabilities improvement patrols.




Conducting training (workshops)
For the education on quality, management system training is conducted in the fourth year, in addition to new employee training, third-year training, fifth-year training, tenth-year training, and middle managers training, all of which are collective education carried out across the company annually.
Subsequently to the previous term, the building department conducted the “education caravan” for employees of all field offices with the aim of eliminating risks (those to quality) that could undermine the company’s credibility (conducted by Teams due to the COVID-19 pandemic).
As a new approach, we conducted education for improving the ability of individuals, which is intended to improve the technical ability of field office employees, for each level. In addition, we continue to conduct the workshops for cooperating companies.
[1] Education caravan
Regarding the past serious quality defects, land pollution which can easily lead to reputation risk, and actual cases at other companies, we have made their causes and recurrence prevention measures known to the employees and ensured recurrence prevention. In addition, we conducted a follow-up education about the rules (Maeda Standards, Construction Management table) that the Building Division of Maeda Corporation created based on the past defects and reputation risk.
Last year, the education caravan was made known and conducted for 950 employees mainly involved in construction works at field offices (and additionally, for 49 temporary workers and 142 employees of the design department).

[2] Education for improving the ability of individuals
Since FY2019, we have continuously conducted “education for improving the ability of individuals,” which is intended to improve the technical abilities of field office employees. In the previous term, for the employees in the positions lower than directors, we conducted the education about the “steel-frame work” and “concrete work” specified in the revised Guidelines on Construction Technology by Type of Work (MAEDA version), in which various expertise about construction works have been compiled. Before the revision of the Guidelines on Construction Technology, various technical materials were scattered and it was difficult to get a target material. Therefore, we revised it with the intention of improving the situation and promoting the utilization of technical materials. The education was conducted by level, for young employees (in their 10th year and under) and middle-level employees (in their 11th year and over) three times each, and a total of 498 employees, 222 young employees, and 276 middle-level employees participated in the education.

[3] Workshops for cooperating companies
For employees and foremen of the cooperating companies, we held workshops on quality based on the case examples of failures that occurred in fields. In the workshops, we used the excerpts of our company's own “Maeda Standards (20 standards in total)” intended to provide value-added quality and the “MAEDA Rules (55 items in total),” which our company and the cooperating companies decided to ensure quality assurance and improve productivity, and made the contents known to the participants. At the same time, we also conducted safety education including lectures on BIM/ICT (Teams webinar was held).
The familiarization and implementation of this education were conducted for 263 cooperating companies (348 people) of our branches.

Efforts to improve quality by using BIM
Building field offices have started efforts, such as productivity improvement and quality improvement, by using BIM at the construction stage (hereinafter referred to as "construction BIM"). Approximately 60% of field offices in operation use the construction BIM. By reproducing the situation of construction completion in a BIM virtual space and thoroughly carrying out adjustment with the parties to be involved in construction prior to construction commencement, we reduce failures after construction commencement.

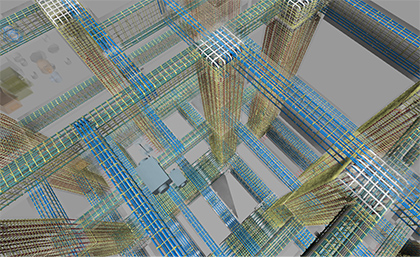
The construction BIM uses a fabrication drawing-level BIM model created by a field office or a specialized contractor. The interaction with the framework of a building, equipment ducts, and pipes, which cannot be seen after completion, is confirmed, and a consensus is formed at a BIM coordination meeting, in which the parties involved in the construction (owner, designer, cooperative companies, and MAEDA) participate.
We are also working on the approach of describing data such as the positions of outlets/switches in the BIM model, and asking the client and others for their opinions about the image after completion and the usability of such fixtures. In addition, in our efforts for structural frameworks, we are also working on bar arrangement BIM, which is intended to study whether or not the assembly can be performed according to the prescribed rule by creating BIM models of beam-to-column connections, irregular framework shapes and reinforcement shapes, and on construction plan BIM, which is intended to reduce failures at the construction stage by sharing a specific image of the construction plan among those involved in the construction by simulating the construction procedures in advance.
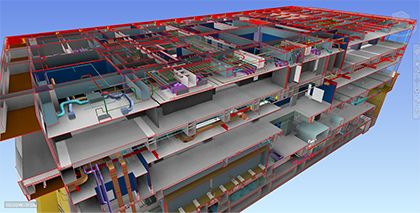

It was confirmed that such efforts for the construction BIM enable the reduction of repair or rework under construction and the prevention of the occurrence of quality failures after completion. The effects were also confirmed that resulted in time savings for drawing examination (20 to 30% reduction) and flexible arrangements of factory manufacturing and preparations for construction by the early approval of fabrication drawings. In FY 2020, we started the front loading project, in which consensus is formed at an early stage of a project to reduce reworking or repair in downstream processes and improve productivity in the entire construction.
To encourage our field offices to practice the construction BIM approach, we have been pursuing education on thorough in-house familiarization for all levels from new employees to field office managers since FY 2017, and plan to promote this approach so that many field offices can implement construction control using BIM.
Improvement of work efficiency by TPM [AX system for bar arrangement (Bar arrangement inspection sheet preparation system)]
The use of the ‘AX system for bar arrangement’ is expected to substantially reduce the time and effort required to prepare a “bar arrangement inspection sheet.” Since an “inspection sheet” is mechanically prepared, human errors are also substantially reduced.
Specifically, the framing plan and parts list in the design drawing CAD data are automatically cut out and put in the “bar arrangement inspection sheet” in Excel, and the figures on the framing plan and the parts list are automatically connected by leader lines (see the figure below.) The inspection sheet is output as Excel data and fine adjustments can be made.
In the construction of a condominium, we are requested by the ordering party to keep a total inspection record with a “bar arrangement inspection sheet.” So far, the staff of the field office prepared the “bar arrangement inspection sheet” and the task was a heavy burden. In addition, the content of the record was checked for errors by a third party such as a supervisor and it took time to complete the sheet.
By introducing this system, we can substantially reduce human errors and save labor (90% reduction). At a field office, the staff can concentrate on the inspection work, resulting in an improvement of work efficiency. Furthermore, since the “inspection sheet” is completed early, it can be commonly used in the inspection by the cooperating companies, internal inspection, and supervisor's inspection.
